Forex

In the financial world, the foreign exchange market, also known as FX, is considered the largest market. Daily volume exceeds $6 trillion.
Compared to other major markets, the FX market is larger than the New York, Tokyo, and London stock exchanges. However, retail trading represents only about $1.69 trillion of $6 trillion.
- Originally, forex trading was only about currency assets, but most platforms now offer a wide variety of assets.
- It involves buying and selling currency assets. There are no physical assets being traded. Exchange rates between two currencies are increasing and decreasing, enabling traders to profit.
- Through a broker, currencies are traded; for example, the U.S. Dollar against the Canadian Dollar (USD/CAD).
- Regardless of whether one currency increases or decreases in value over another, traders only have one goal: to make money.
Forex advantages over stocks
- There are no commissions, clearing fees, exchange fees, government fees, or brokerage fees.
- There are no middlemen, anyone can trade directly with the market on a particular currency pair.
- Leveraged accounts, give the opportunity for traders to participate with small accounts.
- A 24-hour market, no need to wait for the opening bell.
- It is impossible to corner the market, the forex market has so many participants that no single entity can control the market.

Market and Liquidity

- The liquidity of Forex makes it very easy for anyone to buy and sell currencies. There is no limit to the amount one can trade.
- The liquidity of a market determines how easily the price can fluctuate over a given period. In a liquid market such as forex, large trade volumes are allowed to happen without affecting prices or price action.
The details
- Spread
- Buy & Sell
- Pips
- Leverage
It is the difference between a quote (bid) and a purchase price (sell). Because spread is the pricing method of two derivatives, it is a key part of CFD trading. A broker, market maker, or another supplier might quote prices in the form of a spread. Therefore, the price of buying an asset is always higher than the underlying market, and the price of selling an asset is always lower than the underlying market.
It is also a strategy used in options trading,* called option spread. In this case, you buy and sell the same number of options with different strike prices and expiration dates
The purpose of foreign exchange trading is simple. Just like any other form of speculation, you want to buy a currency at a price and sell it at a higher price (or sell a currency at a price and buy it at a lower price) to make a profit. Of course, since the price of one currency is always determined in another currency, there may be some confusion. For example, if the exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar is exactly 2, then the price of one pound sterling can be measured in two U.S. dollars. In foreign exchange trading terms, this value of the British pound will be expressed as the 2.0000 prices of the foreign exchange pair GBP/USD. Currencies are grouped to show the exchange rate between two currencies; in other words, the price of the first currency in the second currency.
The unit of measurement to indicate the change in value between two currencies:
A “Pip.” example if EUR/USD moves from 1.2535 to 1.2536, that .0001 USD rise in value is ONE PIP.
The last decimal of the quotation is the PIP.
Most pairs have 4 decimal places, but there are some exceptions like Japanese Yen pairs which have two decimal places, and fractional pips which add 5 and 3 decimal places.
Simply put: It will be the last digit on any quoted price.
The term leverage is used to describe foreign exchange leverage, in which a broker lends money to a trader for them to trade with more than they initially deposited. It is expressed as a ratio.
Major Pairs

All contain the U.S. dollar on one side and are the most often traded currency pairs and the most liquid.
The major pairs are the most heavily traded currency pairs in the Forex Market.
EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, USD/CAD, AUD/USD, NZD/USD
Currency pairs that don’t contain the U.S. dollar are referred to as “crosses.”
Major crosses are referred to as “minors.”
Most actively traded crosses are from the three major non-USD currencies: GBP, JPY, and EUR.
Exotic pairs are made from one major currency paired with the currency of an emerging economy, like Brazil or Mexico.


The USD is the most frequently traded currency
- Has almost 85% of all transactions
- The euro’s share comes in second around 39%
- The Yen rounds out third with around 19%.
The USD is one-half of every major currency pair, and the majors comprise 75% of all trades.
The USD is one half of every major currency pair and the majors comprise 75% of all
Three ways
- Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
The framework in which traders study price movement. The theory is that a person can look at historical price movements and determine the current trading conditions and potential price movement.
“History tends to repeat itself”
“It’s all about the charts”
Technical analysts look for similar patterns that have formed in the past and will form trade ideas believing that price will act the same way that it did before.
In the world of trading, when someone says technical analysis, the first thing that comes to mind is a chart. Technical analysts use charts because they are the easiest way to visualize historical data!
Analyzing the economy, that will affect, supply and demand of an asset.
Using supply and demand as an indicator of where price might be moving.
The hard part is analyzing all the factors that affect supply and demand.
You have to know the reasons why and how certain events like an increase in unemployment affect a country’s economy, and ultimately, the level of demand for its currency.
The main idea is that a country’s current or future economic outlook is going well, its currency should strengthen. The better shape of a country’s economy is, the more foreign businesses and investors will invest within the country.
This results in purchasing that country’s currency to obtain assets.
It’s all about feelings. You already know the terms, Bull(ish) or Bear(ish).
If a trader chooses to ignore market sentiment, it’s almost always a certain fail.
No matter how clear that chart looks and how good that news is coming out of Reuters. If the market is Bearish the rate won’t move that drastically upward.
Fun fact: a bull’s horns go up when charging so to say bullish means the markets are up. A bear’s claws go down when charging so to say bearish means the markets are down.
Market Movers
- Unemployment Rate
- Non-Farm Payroll
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Producer Price Index
- Rate Announcements
- Interest Rate
- Current Account
- Asset Purchases
- German IFO business climate Index
The percentage of the total workforce that is unemployed but actively seeking employment and willing to work during the previous month.
It is released monthly, every first Friday of a new month on the same day that the Non-Farm Payroll is released.
Actual < Forecast = Good for the currency
Measures the change in the number of employed people during the previous month, excluding the new
job openings in the agricultural sector because these positions are seasonal.
It is released monthly, every first Friday of a month. Also called Non-Farm Employment Change,
NFP and Employment Change. When the numbers are released the market experiences strong volatility.
It is considered one of the most important leading indicators.
Actual > Forecast = Good for the
currency
Measures the change within the inflation-adjusted value of all goods and services produced by the economy. It is an indicator that says a lot about the health of the economy of a country and it always moves the markets. (Look at the GDP releases of the most important economic powers).
It is released quarterly, about 30 days after the quarter ends. GDP has three versions released a
month apart – Advance, Preliminary, and Final. The most Advance release is the earliest and thus tends to have the most impact.
Actual > Forecast = Good for currency
Measures the change in the price of goods and services purchased by consumers. (16.9.2015) U.S
consumer prices fell in August as oil prices fell and a strong dollar curbed the prices of goods.
Strong dollar, weak petrol, and gold prices (almost a rule).
It is released monthly, about 16 days after the month ends.
Actual > Forecast = Good for currency
Measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time.
It is released monthly, about 14 days after the month ends.
Actual > Forecast = Good for currency
Interest rates on the main refinancing operations provide the bulk of liquidity to the banking system.
For the European Central Bank (EU) and the Federal Reserve (US) it’s scheduled 8 times per year and for the Bank of England (UK) it’s scheduled monthly.
Actual > Forecast = Good for currency
Deflation reflects an increase in the purchasing power of money thus prices decreased. When interest rates are cut, fundamentally currency gets weaker and at the same time stocks go up. When interest rates hike, fundamentally currency gets stronger and at the same time stocks go down.
It is defined as the sum of the balance of trade (goods and services export fewer imports), net income from abroad, and net current transfers. A positive current account balance indicates that the nation is a
net lender to the rest of the world, while a negative current account balance indicates that it is a net borrower from the rest of the world. (U.S, Japan, Germany)
Indicates strong economic expansion
The total value of money that the Central Bank will create and use to purchase assets in the open market.
For the European Central Bank (EU) and the Federal Reserve (US) it’s scheduled 8 times per year and for the Bank of England (UK) it’s scheduled monthly.
Actual < Forecast = Good for currency
Level of a composite index based on surveyed manufacturers, builders, wholesalers, and retailers. A key survey that measures the business climate in Germany. It is widely followed as an early indicator of the state of the German economy. The Ifo Business Climate Survey is based on approximately 7,000
monthly survey responses from firms in manufacturing, construction, wholesale, and retail.
Released monthly, around 3 weeks into the current month.
Actual > Forecast =
Good for currency
Charts
Line Chart
A simple line chart draws a line from one closing price to the next closing price. When strung together with a line, we can see the general price movement of a currency pair over a period of time.

Bar Chart
The bar chart shows the opening and closing, highs and lows prices, of an asset or over a specified time.
The bottom of the vertical bar designates the lowest traded price for that time, The top of the bar designates the highest price paid.
The vertical bar itself indicates the currency pair’s trading range of high and low prices for the period.
The horizontal hash on the left side and right side of the bar is the opening price and the closing price.
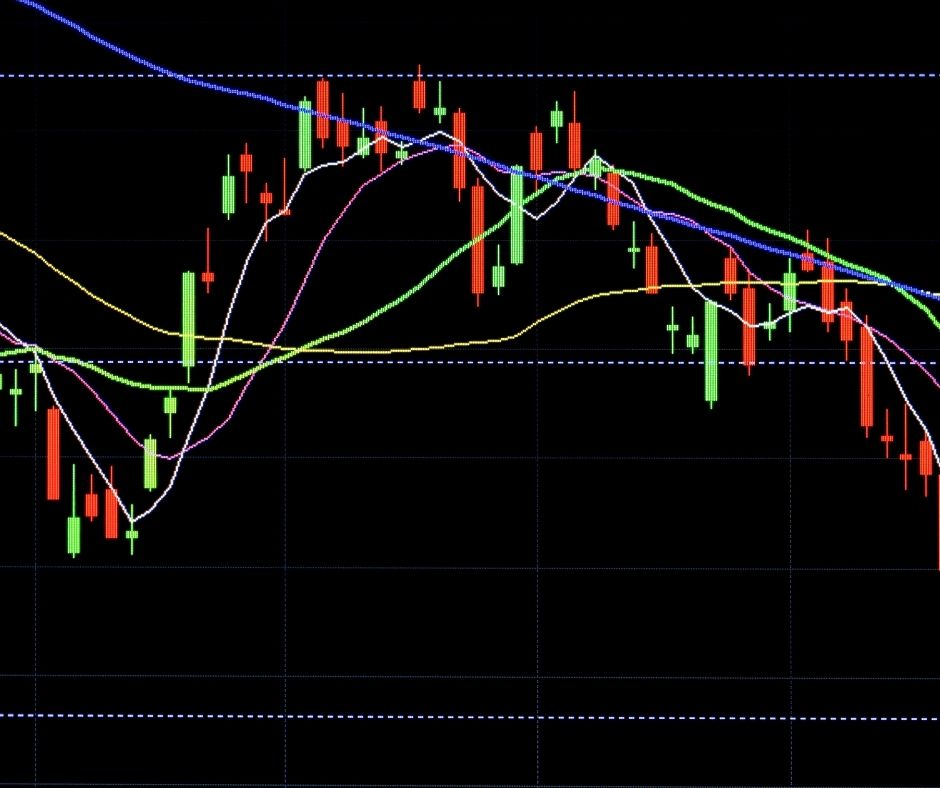
Candlestick
Candlestick bars designate the high to the low range with a vertical line. The larger body in the middle designates the range between the opening and closing prices.
If the middle is red, then the currency pair closed lower than it opened.
If the middle is green, then the currency pair closed higher than it opened





